what happens to cells when insulin is increased
Type 1 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there is a high level of sugar (glucose) in the claret.
Type 1 diabetes tin occur at any age. It is about frequently diagnosed in children, adolescents, or immature adults.
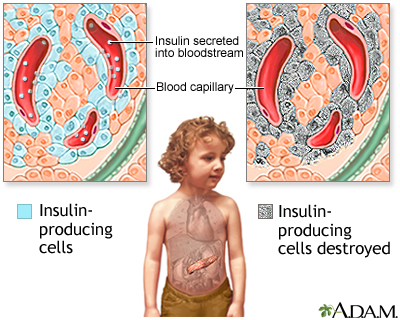
Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas past special cells, called beta cells. The pancreas is below and behind the stomach. Insulin is needed to move blood sugar (glucose) into cells. Inside the cells, glucose is stored and later used for energy. With type 1 diabetes, beta cells produce niggling or no insulin.
Without enough insulin, glucose builds upwards in the bloodstream instead of going into the cells. This buildup of glucose in the claret is chosen hyperglycemia. The body is unable to use the glucose for free energy. This leads to the symptoms of type 1 diabetes.
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown. Virtually likely, it is an autoimmune disorder. This is a status that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. With blazon one diabetes, an infection or some other trigger causes the trunk to mistakenly attack the beta cells in the pancreas that make insulin. The tendency to develop autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes, can be inherited from your parents.
High Blood Saccharide
The post-obit symptoms may be the showtime signs of type ane diabetes. Or, they may occur when blood sugar is high.
- Being very thirsty
- Feeling hungry
- Feeling tired all the time
- Having blurry eyesight
- Feeling numbness or tingling in your feet
- Losing weight despite an increased appetite
- Urinating more oft (including urinating at dark or bedwetting in children who were dry overnight earlier)
For other people, these serious warning symptoms may be the get-go signs of blazon 1 diabetes. Or, they may happen when blood saccharide is very high (diabetic ketoacidosis):
- Deep, rapid breathing
- Dry peel and mouth
- Flushed face
- Fruity breath aroma
- Nausea and vomiting; disability to keep down fluids
- Breadbasket pain
Depression BLOOD Carbohydrate
Depression blood carbohydrate (hypoglycemia) can develop quickly in people with diabetes who are taking insulin. Symptoms usually appear when a person's blood sugar level falls beneath 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or iii.nine mmol/L. Sentinel for:
- Headache
- Hunger
- Nervousness, irritability
- Rapid heartbeat (palpitations)
- Shaking
- Sweating
- Weakness
Afterward many years, diabetes can atomic number 82 to serious health bug, and as a result, many other symptoms.
Diabetes is diagnosed with the post-obit blood tests:
- Fasting blood glucose level -- Diabetes is diagnosed if it is 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher 2 different times.
- Random (not-fasting) claret glucose level -- You may have diabetes if information technology is 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or college, and you take symptoms such as increased thirst, urination, and fatigue. (This must be confirmed with a fasting examination.)
- Oral glucose tolerance test -- Diabetes is diagnosed if the glucose level is 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/50) or college 2 hours after you drinkable a special sugar drink.
- Hemoglobin A1C (A1C) test -- Diabetes is diagnosed if the effect of the test is 6.5% or college.
Ketone testing is also used sometimes. The ketone test is done using a urine sample or blood sample. Ketone testing may be washed to determine if someone with type 1 diabetes has had ketoacidosis. Testing is usually done:
- When the blood sugar is higher than 240 mg/dL (13.3 mmol/Fifty)
- During an illness such every bit pneumonia, heart attack, or stroke
- When nausea and vomiting occur
- During pregnancy
The following exams and tests will help you and your health are provider monitor your diabetes and preclude problems caused past diabetes:
- Check the skin and bones on your anxiety and legs.
- Check if your anxiety are getting numb (diabetic nerve disease).
- Have your claret pressure checked at least once a twelvemonth. The goal should be 140/90 mmHg or lower.
- Have an A1C examination washed every half dozen months if your diabetes is well controlled. Have the test done every 3 months if your diabetes is non well controlled.
- Have your cholesterol and triglyceride levels checked once a year.
- Get tests in one case a year to make certain your kidneys are working well. These tests include checking levels of microalbuminuria and serum creatinine.
- Visit your eye physician at least once a year, or more than often if you accept signs of diabetic eye disease.
- See the dentist every six months for a thorough dental cleaning and test. Make certain your dentist and hygienist know that yous have diabetes.
Considering type i diabetes can start rapidly and the symptoms can be astringent, people who have just been diagnosed may need to stay in the hospital.
If yous have just been diagnosed with type ane diabetes, you may need to have a checkup each week until y'all have skillful control over your blood saccharide. Your provider will review the results of your home claret carbohydrate monitoring and urine testing. Your doctor volition also await at your diary of meals, snacks, and insulin injections. It may have a few weeks to match the insulin doses to your meal and activity schedules.
As your diabetes becomes more than stable, yous will take fewer follow-upwardly visits. Visiting your provider is very of import and so you lot can monitor any long-term problems from diabetes.
Your provider will likely enquire you to see with a dietitian, clinical pharmacist, and certified diabetes care and didactics specialist (CDCES). These providers will likewise assist you lot manage your diabetes.
But, you are the almost of import person in managing your diabetes. You should know the basic steps of diabetes direction, including:
- How to recognize and treat low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- How to recognize and treat high blood carbohydrate (hyperglycemia)
- How to plan meals, including carbohydrate (carb) counting
- How to give insulin
- How to bank check claret glucose and urine ketones
- How to adapt insulin and food when yous exercise
- How to handle ill days
- Where to buy diabetes supplies and how to store them
INSULIN
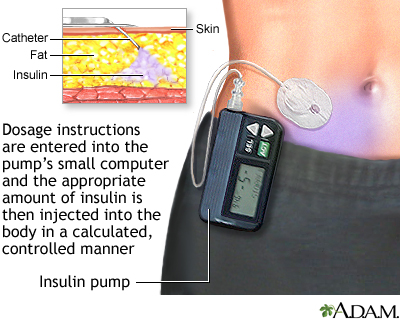
Insulin lowers blood sugar by allowing it to go out the bloodstream and enter cells. Everyone with type ane diabetes must take insulin every solar day.
Most commonly, insulin is injected under the skin using a syringe, insulin pen, or insulin pump. Another class of insulin is the inhaled type. Insulin cannot be taken by oral fissure considering the acid in the tum destroys insulin.
Insulin types differ in how fast they showtime to piece of work and how long they terminal. Your provider volition choose the best type of insulin for you and will tell you lot at what time of day to utilise information technology. Some types of insulin may be mixed together in an injection to go the all-time claret glucose command. Other types of insulin should never exist mixed.
About people with type i diabetes need to take two kinds of insulin. Basal insulin is long-lasting and controls how much sugar your own trunk makes when you are not eating. Meal-time (nutritional) insulin is rapid interim and is taken with every meal. It lasts simply long enough to help move the sugar captivated from a meal into musculus and fat cells for storage.
Your provider or diabetes educator volition teach you how to requite insulin injections. At first, a kid's injections may be given by a parent or another adult. By age fourteen, most children can give themselves their ain injections.
Inhaled insulin comes as a pulverisation that is breathed in (inhaled). It is rapid acting and used but before each repast. Your provider tin can tell you if this blazon of insulin is right for you lot.
People with diabetes need to know how to conform the corporeality of insulin they are taking:
- When they exercise
- When they are sick
- When they will be eating more or less food and calories
- When they are traveling
Good for you EATING AND EXERCISE
By testing your blood sugar level, you can learn which foods and activities enhance or lower your claret saccharide level the most. This helps yous adjust your insulin doses to specific meals or activities to prevent blood sugar from becoming too high or too low.
The American Diabetes Association and the Academy of Diet and Dietetics have data for planning healthy, counterbalanced meals. Information technology likewise helps to talk to a registered dietitian or diet counselor.
Regular exercise helps command the amount of sugar in the blood. It also helps burn extra calories and fat to reach and maintain a healthy weight.
Talk to your provider earlier starting whatever do program. People with type i diabetes must take special steps earlier, during, and after concrete activity or exercise.
MANAGING YOUR Blood SUGAR
Checking your blood saccharide level yourself and writing downward the results tells you how well you are managing your diabetes. Talk to your provider and diabetes educator well-nigh how often to check.
To check your blood sugar level, you use a device called a glucose meter. Usually, you prick your finger with a small needle, called a lancet, to get a tiny drop of blood. You lot place the blood on a examination strip and put the strip into the meter. The meter gives yous a reading that tells you the level of your blood carbohydrate.
Continuous glucose monitors mensurate your blood sugar level from fluid under your skin. These monitors are used mostly by people who are on insulin pumps to control their diabetes. Some monitors do not require a finger prick.
Go along a record of your blood sugar for yourself and your wellness care squad. These numbers will help if you take problems managing your diabetes. Y'all and your provider should set a target goal for your blood saccharide level at different times during the 24-hour interval. You lot should besides programme what to do when your blood sugar is besides low or high.
Talk to your provider about your target for the A1C test. This lab test shows your boilerplate blood sugar level over the past three months. It shows how well you are controlling your diabetes. For most people with type ane diabetes, the A1C target should be seven% or lower.
Low claret sugar is called hypoglycemia. A blood sugar level below lxx mg/dL (three.9 mmol/L) is too low and can damage you. A claret saccharide level below 54 mg/dL (three.0 mmol/L) is cause for immediate activity. Keeping good control of your blood carbohydrate can help prevent depression blood carbohydrate. Talk to your provider if you're not sure about the causes and symptoms of low blood saccharide.
Human foot CARE
People with diabetes are more likely than those without diabetes to accept foot problems. Diabetes damages the nerves. This tin can brand your anxiety less able to feel pressure, pain, rut, or cold. You may non notice a human foot injury until y'all have severe damage to the skin and tissue beneath, or you become a severe infection.
Diabetes can also damage claret vessels. Small sores or breaks in the skin may become deeper peel sores (ulcers). The afflicted limb may need to be amputated if these skin ulcers do not heal, or get larger, deeper, or infected.
To preclude bug with your feet:
- Stop smoking, if y'all fume.
- Better control of your blood carbohydrate.
- Get a foot exam at least twice a year from your provider, and acquire whether you take nerve damage.
- Ask your provider to check your feet for issues such as calluses, a bunion or hammertoe. These demand to be treated to prevent pare breakdown and ulcers.
- Bank check and care for your anxiety every day. This is very important when yous already have nerve or claret vessel damage or foot problems.
- Treat minor infections, such equally athlete's foot, right away.
- Skillful nail care is important. If your nails are very thick and hard, yous should have your nails trimmed by a podiatrist or other provider who knows you accept diabetes.
- Use moisturizing balm on dry out skin.
- Make sure you lot vesture the right kind of shoes. Ask your provider what kind is right for you.
PREVENTING COMPLICATIONS
Your provider may prescribe medicines or other treatments to reduce your chances of developing common complications of diabetes, including:
- Center disease
- Kidney disease
- Peripheral nerve damage
- Heart affliction and stroke
With type i diabetes, you are also at risk of developing conditions such as hearing loss, gum affliction, bone disease, or yeast infections (in women). Keeping your blood saccharide under practiced control can aid prevent these conditions.
Talk with your health care team about other things you tin practice to lower your chances of developing diabetes complications.
People with diabetes should brand sure to keep up on their vaccination schedule.
EMOTIONAL HEALTH
Living with diabetes tin can be stressful. You may feel overwhelmed by everything you need to do to manage your diabetes. Simply taking care of your emotional wellness is merely as of import as your concrete health.
Ways to salvage stress include:
- Listening to relaxing music
- Meditating to have your mind off your worries
- Deep breathing to help relieve physical tension
- Doing yoga, tai chi, or progressive relaxation
Feeling sad or down (depressed) or anxious sometimes is normal. But if you accept these feelings oftentimes and they're getting in the manner of managing your diabetes, talk with your health care team. They can find ways to help yous experience better.
At that place are many diabetes resources that can help you understand more than most type ane diabetes. You can besides acquire ways to manage your condition and so that yous can live well with diabetes.
Diabetes is a lifelong affliction and in that location is no cure.
Tight control of claret glucose can forbid or filibuster diabetes complications. Merely these problems can occur, even in people with adept diabetes control.
After many years, diabetes can lead to serious health bug:
- You could take center problems, including trouble seeing (specially at night) and sensitivity to calorie-free. You lot could become blind.
- Your feet and skin could develop sores and infections. If you have these sores for too long, your foot or leg may need to be amputated. Infection can also cause pain, swelling, and itching.
- Diabetes may make information technology harder to control your blood pressure and cholesterol. This can atomic number 82 to heart attack, stroke, and other problems. Information technology tin become harder for claret to catamenia to the legs and feet.
- Diabetes tin can weaken your allowed system and make it more likely for you to come down with infections.
- Fretfulness in the torso tin can get damaged, causing pain, itching, tingling, and numbness.
- Because of nervus damage, you could have problems digesting the nutrient you lot eat. You could experience weakness or have trouble going to the bathroom. Nerve harm can also make information technology harder for men to take an erection.
- Loftier blood sugar and other issues can lead to kidney damage. The kidneys may not work also as they used to. They may even stop working, then that you would demand dialysis or a kidney transplant.
- High claret sugar tin can weaken your immune organization. This may make information technology more than likely for you to get infections, including life-threatening skin and fungal infections.
Phone call 911 or the local emergency number if you take:
- Chest hurting or pressure, shortness of breath, or other signs of angina
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
Phone call your provider or become to the emergency room if you have symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis.
Also telephone call your provider if you have:
- Claret saccharide levels that are college than the goals you and your provider have set
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in your feet or legs
- Problems with your eyesight
- Sores or infections on your feet
- Frequent feelings of depression or feet
- Symptoms that your blood sugar is getting as well low (weakness or fatigue, trembling, sweating, irritability, trouble thinking clearly, fast heartbeat, double or blurry vision, uneasy feeling)
- Symptoms that your blood sugar is too high (thirst, blurry vision, dry peel, weakness or fatigue, need to urinate a lot)
- Claret sugar readings that are below seventy mg/dL (3.nine mmol/Fifty)
Yous can care for early signs of hypoglycemia at home by drinking orangish juice, eating sugar or candy, or past taking glucose tablets. If signs of hypoglycemia continue or your claret glucose level stays beneath 60 mg/dL (iii.iii mmol/L), go to the emergency room.
Type one diabetes cannot exist prevented currently. This is a very active expanse of research. In 2019, a study using an injectable medication was able to delay the onset of type ane diabetes in high-risk children. There is no screening exam for blazon 1 diabetes in people who have no symptoms. However, antibiotic testing can identify children at higher chance of developing blazon ane diabetes if they accept outset-degree relatives (sibling, parent) with type 1 diabetes.
Insulin-dependent diabetes; Juvenile onset diabetes; Diabetes - type i; High blood carbohydrate - type 1 diabetes
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Intendance in Diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021 Jan;44(Suppl 1):S15-S33. PMID: 33298413 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33298413/.
Atkinson MA, Mcgill DE, Dassau E, Laffel L. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. In: Melmed S, Auchus, RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 36.
Brownlee Chiliad, Aiello LP, Sun JK, et al. Complications of diabetes mellitus. In: Melmed Southward, Auchus, RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 37.
Updated past: Brent Wisse, MD, board certified in Metabolism/Endocrinology, Seattle, WA. Internal review and update on 06/04/2021 by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Managing director, and the A.D.A.Chiliad. Editorial team.
littlefieldmonce1990.blogspot.com
Source: https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000305.htm
0 Response to "what happens to cells when insulin is increased"
Post a Comment